Static maps for Germany
mappingDE.RdFunction to produce static maps for Germany statistical unit.
Usage
mappingDE(data, var = NULL, colID = NULL,
type = c("static", "interactive"),
typeStatic = c("tmap", "choro.cart", "typo", "bar"),
unit = c("state", "district", "municipal", "municipality"),
matchWith = c("name", "code", "code_full"), dir = NULL,
add_text = NULL, subset = NULL, facets = NULL,
aggregation_fun = sum, aggregation_unit = NULL,
options = mapping.options())Arguments
- data
a data.frame object with variables to display or a
DEobject produced byDEfunction. If object of classDE, argumentsunit,year, andmatchWithwill be ignored- var
character value(s) or columns number(s) indicating the variable to plot
- colID
character value or columns number indicating the column with unit names
- type
if generates static or interactive map
- typeStatic
type of static map
- unit
the type of Italian statistical unit
- matchWith
the type of id to check:
"name"if unit names "code"if unit code "code_full"if unit complete code - dir
local directory in which shape files are stored
- add_text
character name indicating the column with text labels
- subset
a formula indicating the condition to subset the data. See the details section
- facets
variable(s) name to split the data
- aggregation_fun
function to use when data are aggregated
- aggregation_unit
variable name by which the unit are aggregated
- options
a list with options using
mapping.optionsfunction
Details
If data is a object of class "DE" generated using the DE function, the argument unit, because the object already contains the coordinates.
The aggregation_unit provides an aggregation for a user specified variable in data, or for larger statistical unit, automatically provided when the function link the data with the coordinates. For example, if data are of type municipal, we will have variables for larger aggregate unit, that is district and state variables. Look at DE for more details.
subset provide an expression to subsetting the data using a formula, with the logical operators. For example data can be subsetting as follows: ~I("Variable 1" == "condition 1" & "Variable 2" != "condition 2") or for example, ~I("Variable 1" > "condition 1" | "Variable 2" != "condition 2").
Examples
data("popDE")
de <- DE(data = popDE, colID = "code_state",
unit = "state", matchWith = "code_full",
check.unit.names = FALSE)
# \donttest{
###############
# Statics #
###############
mappingDE(data = de, var = "population_2020")
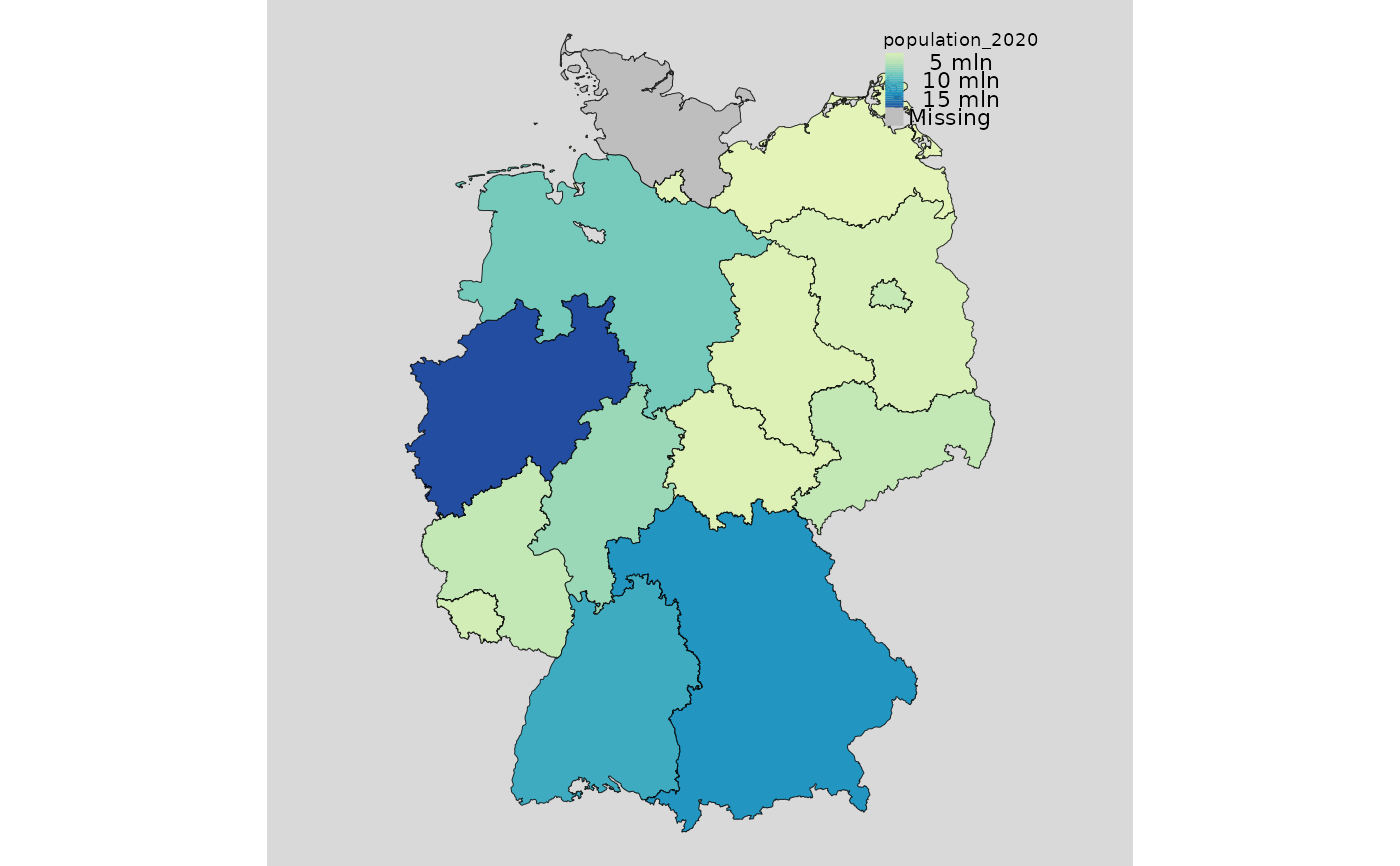 mappingDE(data = de, var = "population_2020",
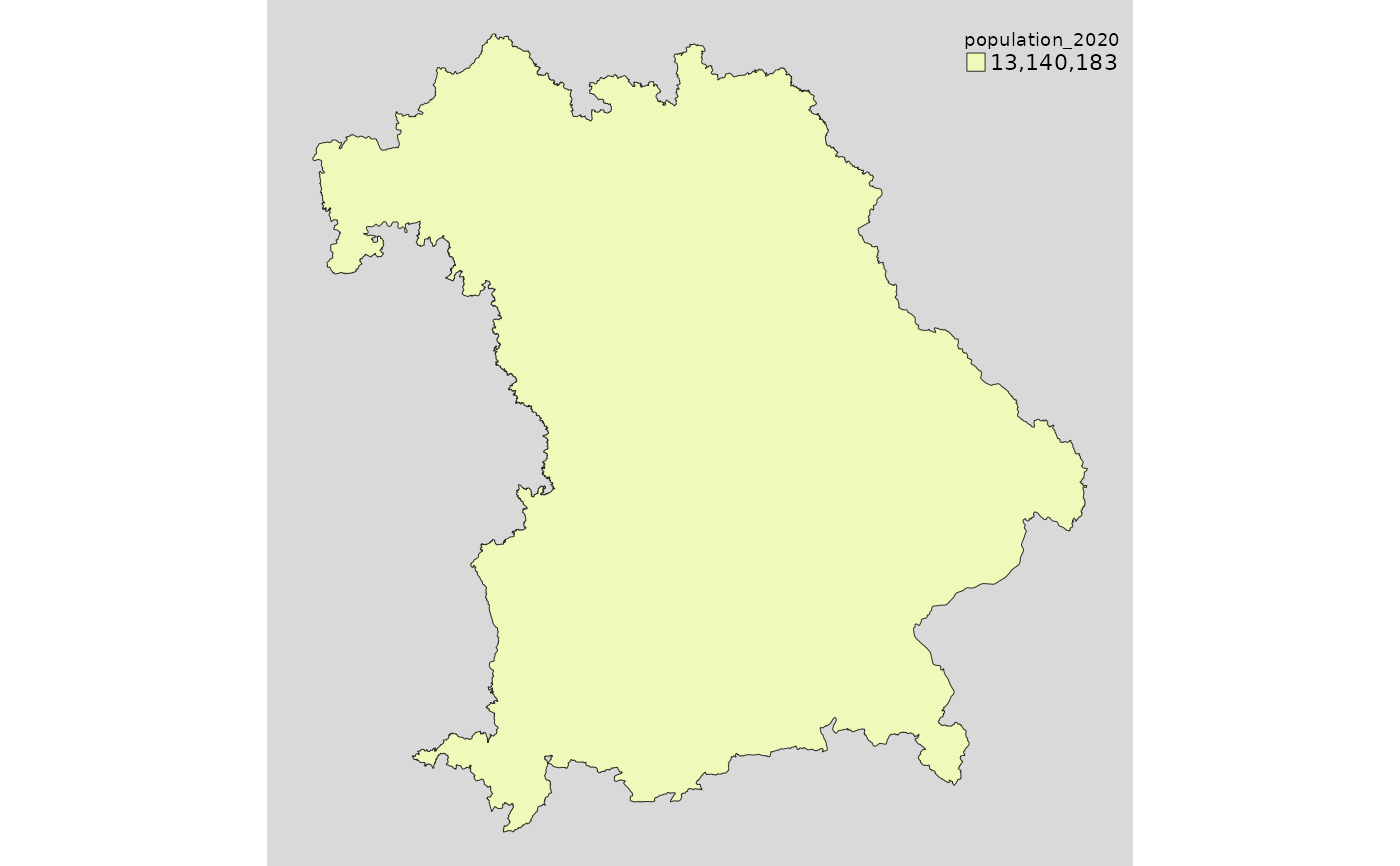
subset = ~I(state == "bayern"))
mappingDE(data = de, var = "population_2020",
subset = ~I(state == "bayern"))
 # }
###############
# Interactive #
###############
mappingDE(data = de, var = "population_2020", type = "interactive")
# \donttest{
mappingDE(data = de, var = "population_2020",
subset = ~I(state == "bayern"),
type = "interactive")
# }
# }
###############
# Interactive #
###############
mappingDE(data = de, var = "population_2020", type = "interactive")
# \donttest{
mappingDE(data = de, var = "population_2020",
subset = ~I(state == "bayern"),
type = "interactive")
# }